Part 1.笔记
单调栈
模版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 void findRMin (int n,int a[],int b[]) stack<pair<int ,int >> q; for (int i=n;i>=1 ;i--) { while (!q.empty ()&&a[i]<=q.top ().first) q.pop (); if (q.empty ()) b[i]=0 ; else b[i]=q.top ().second; q.push (make_pair (a[i],i)); } } void findLMin (int n,int a[],int b[]) stack<pair<int ,int >> q; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) { while (!q.empty ()&&a[i]<=q.top ().first) q.pop (); if (q.empty ()) b[i]=0 ; else b[i]=q.top ().second; q.push (make_pair (a[i],i)); } } void findRMax (int n,int a[],int b[]) stack<pair<int ,int >> q; for (int i=n;i>=1 ;i--) { while (!q.empty ()&&a[i]>=q.top ().first) q.pop (); if (q.empty ()) b[i]=0 ; else b[i]=q.top ().second; q.push (make_pair (a[i],i)); } } void findLMax (int n,int a[],int b[]) stack<pair<int ,int >> q; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) { while (!q.empty ()&&a[i]>=q.top ().first) q.pop (); if (q.empty ()) b[i]=0 ; else b[i]=q.top ().second; q.push (make_pair (a[i],i)); } }
解释
以寻找右边第一个比自己小的元素的坐标为例,从最后一个元素开始从右往左遍历,栈q中按照从顶到底降序存储。
字典树Trie Tree
模版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 struct trie { int next[26 ]; int isEnd; }tree[500005 ]; int inc; int insert (string s) int p=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s.size ();i++) { if (tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]) p=tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]; else { inc++; tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]=inc; p=inc; } } if (tree[p].isEnd) return 1 ; else tree[p].isEnd=1 ; return 0 ; } int check (string s) int p=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s.size ();i++) { if (!tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]) return 0 ; p=tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]; } if (tree[p].isEnd) return 1 ; return 0 ; }
解释
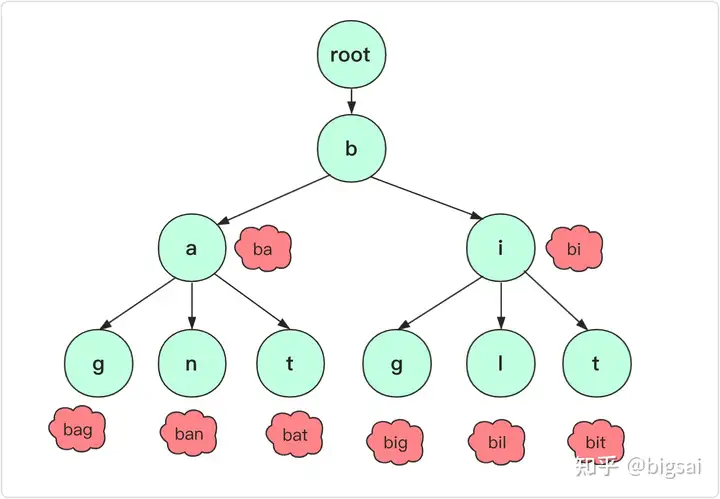
字典树,是一种空间换时间 的数据结构,又称Trie树、前缀树,是一种树形结构,典型用于统计、排序、和保存大量字符串。利用字符串的公共前缀来减少查询时间,最大限度地减少不需要的字符串比较,查询效率比哈希树高。
根节点不包含字符,除根节点外每一个节点都只包含一个字符。
定义结构体:该结构体用来存储树的每一个节点,每个节点都包括了指向子节点的指针,以及当前节点是否为单词的结尾。
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct trie { int next[26 ]; int isEnd; }tree[500005 ]; int inc;
插入单词:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 int insert (string s) int p=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s.size ();i++) { if (tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]) p=tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]; else { inc++; tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]=inc; p=inc; } } if (tree[p].isEnd) return 1 ; else tree[p].isEnd=1 ; return 0 ; }
检查单词是否存在:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 int check (string s) int p=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s.size ();i++) { if (!tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]) return 0 ; p=tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]; } if (tree[p].isEnd) return 1 ; return 0 ; }
并查集
模版
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int n,m,k,x,y;int pre[200005 ];int find (int x) if (x!=pre[x]) pre[x]=find (pre[x]); return pre[x]; } void merge (int a,int b) int x=find (a); int y=find (b); pre[x]=y; } int main () cin>>n>>m; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++) pre[i]=i; for (int i=1 ;i<=m;i++) { cin>>k>>x>>y; if (k==1 ) merge (x,y); if (k==2 ) { int x0=find (x); int y0=find (y); if (x0==y0) cout<<"Y" <<endl; else cout<<"N" <<endl; } } return 0 ; }
解释
并查集是可以快速完成判断两个元素是否在同一集合或者合并两个集合的一种数据结构。
将每一个元素都视为树上的一个节点,每一个集合就是一棵独立的树,指定一个集合中的任意一个元素为根,将其他元素以树的形式连接到这个根上。同时树中的每一个节点都存储着一个指针指向他的父节点。而根节点的父节点指向自己。
并查集有两种基础操作,查找根和合并集合。
查找一个元素的根时,因为每一个元素就是树上的一个节点,而节点记录着自己的父节点,所以可以利用递归顺着记录的父节点不断向上查找,直到找到一个节点其父节点就是他自己,这个节点就是根。
1 2 3 4 5 int find (int x) if (x!=pre[x]) return find (pre[x]); else return x; }
而合并两个集合时,也就是需要将其中一个集合的树连接到到另一个集合的树上,于是查找到其中一个树的根,并将这个根的父节点指向另一个树上的任意元素。
也就是说,合并集合是在查找根的基础上完成的。而查找根时,递归的深度是由当前节点到树根的距离决定的,而并不关系途中经过了哪些节点,即节点距离树根越近,递归深度越低。那么将每一个节点都直接连接在树根上,这是查找树根的速度将是最快的。于是在进行合并操作时,会同时找到要合并的两棵树的根,并将其中的一个根的父节点直接指向另一个根。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 void merge (int a,int b) int x=find (a); int y=find (b); pre[x]=y; }
但这样做并不是最快的,还可以通过路径压缩 使得操作更快一点。在利用递归查找根的同时,当找到根后,根的下标会被一路以返回给上一层函数,即查找过程中经过的子节点,这是就可以将途经的所有节点的父节点都指向根,也就可以使得更多的元素直接连接在根上,这样就完成了对树的压缩。
1 2 3 4 5 6 int find (int x) if (x!=pre[x]) pre[x]=find (pre[x]); return pre[x]; }
所以如果想要判断两个元素是否属于同一集合时,只需要分别查找这两个元素所在树的根,判断根是否一致即可。如果处于不同集合,则根不同。
1 2 3 4 int x0=find (x);int y0=find (y);if (x0==y0) cout<<"Y" <<endl;else cout<<"N" <<endl;
Part 2. 训练题题解
寒假算法训练(一)数据结构基础
#Algo0101.# Look Up S
题目描述
本题为单调栈模版题。每头奶牛向右看,求出每只奶牛离她最近的仰望对象,也就是求出右边第一个大于自己的数。从右往左维护一个严格单增的单调栈即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 int n,a[1000006 ],b[1000006 ];stack<pair<int ,int >> q; int main () CI n; CII (a,1 ,n); FD (i,n,1 ) { while (!q.empty ()&&a[i]>=q.top ().first) q.pop (); if (q.empty ()) b[i]=0 ; else b[i]=q.top ().second; q.push (make_pair (a[i],i)); } F (i,1 ,n) CO b[i] L; return 0 ; }
#Algo0102.# Bad Hair Day S
题目描述
本题求能看见多少个牛的头发,即当牛向右看时,有多少头牛的身高是小于自己的,直到遇到升高大于自己的牛。可以转换以下思路,将看见多少头牛转换为被多少头牛看见自己的头发。能看见自己头发的牛,必然是处于左边且高于自己的牛,而且中间没有比观察者更高的牛阻隔。所以可以从左到右维护一个严格单减的单调栈,而每次维护完栈后,栈中的元素个数便是能看到自己的牛的个数。但是由于STL内置的栈并不能查询栈内元素个数,所以可以在入栈和出栈时进行计数,也可以自己写一套栈的函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 LL n,a[80004 ],ans; struct myStack { int a[80004 ],index=0 ; int empty () { return index==0 ; } int top () { return a[index]; } void push (int x) { a[++index]=x; } void pop () { index--; } int ind () { return index; } } q; int main () CI n; CII (a,1 ,n); F (i,1 ,n) { while (!q.empty ()&&a[i]>=q.top ()) q.pop (); if (!q.empty ()) ans+=q.ind (); q.push (a[i]); } CO ans L; return 0 ; }
#Algo0103.# 玉蟾宫
题目描述
本题需要求由F构成的最大的矩形面积。在求最大矩形面积时,可以利用单调栈来快速找到最大的面积。先选中一行,将每一列视为一个矩形,并求出该行中每一列的F向上最大能延伸的高度为多少,将其定为每一列的高度。这样就将二维中寻找最大矩形面积转换为了给定每个矩形的高度,在其中寻找最大矩形面积。然后对每一行应用一次这样的计算,便能得到最终最大的矩形面积。对于给定每个矩形高度求其中的最大面积,首先需要选中一个矩形高度,并由该高度构成大矩形,这时还需要求出该高度能够得到的最大宽度为多少。最大宽度是根据被选定矩形的左右两边有多少个高度大于它的矩形,也就是需要分别找到左右第一个小于它的高度的矩形。这就将问题又转变为了单调栈问题。可以利用单调栈分别找到左右第一个高度小于被选定矩形的位置,相减就能得到大矩形的宽,然后与高相乘得到面积。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 int n,m,a[1003 ][1003 ],b[1003 ],l[1003 ],r[1003 ],ans;char c;void findRMin (int n,int a[],int b[]) stack<pair<int ,int >> q; FD (i,n,1 ) { while (!q.empty ()&&a[i]<=q.top ().first) q.pop (); if (q.empty ()) b[i]=n+1 ; else b[i]=q.top ().second; q.push (make_pair (a[i],i)); } } void findLMin (int n,int a[],int b[]) stack<pair<int ,int >> q; F (i,1 ,n) { while (!q.empty ()&&a[i]<=q.top ().first) q.pop (); if (q.empty ()) b[i]=0 ; else b[i]=q.top ().second; q.push (make_pair (a[i],i)); } } int main () CI n>>m; F (i,1 ,n) F (j,1 ,m) { CI c; a[i][j]=c=='R' ?0 :1 ; } F (i,1 ,n) { F (j,1 ,m) { b[j]=0 ; FD (k,i,1 ) if (a[k][j]) b[j]++; else break ; } findLMin (m,b,l); findRMin (m,b,r); F (j,1 ,m) { ans=max (ans,b[j]*(r[j]-l[j]-1 )); } } CO ans*3 L; return 0 ; }
#Algo0104.# 滑动窗口
题目描述
该题为单调队列的模版题。最大值和最小值需要分别求解。首先需要两个指针分别指向队列的开头和结尾。从左到右依次遍历每一个元素,在求窗口最小值时,需要从队列末尾中将大于当前元素的元素都移除队列,因为每次遍历时,都意味着当前元素被加入到窗口中,同时也意味着队列中那些大于当前元素的元素都再也不可能成为最小值,所以将其移出队列。同时每次都要判断一次队列头部是否已经超出了窗口了,并移除超出的元素。同时由于队列里的元素严格单调递增,所以队列头部即为当前窗口的最小值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 int n,k,f,h;LL a[1000006 ],p[1000006 ]; int main () CI n>>k; CII (a,1 ,n) f=1 ,h=0 ; F (i,1 ,n) { while (f<=h&&a[p[h]]>=a[i]) h--; p[++h]=i; if (p[f]<i-k+1 ) f++; if (i>=k) CO a[p[f]] P; } CL f=1 ,h=0 ; F (i,1 ,n) { while (f<=h&&a[p[h]]<=a[i]) h--; p[++h]=i; if (p[f]<i-k+1 ) f++; if (i>=k) CO a[p[f]] P; } CL return 0 ; }
#Algo0105.# 合并果子
题目描述
为了以最少体力合并果子,需要每次都找出重量最小的两堆果子进行合并,然后再将合并后的重量加回果子队列,然后进行下一次找出重量最小的两堆果子。对于这种需要多次寻找最小值的操作,可以用优先队列的小根堆来做。优先队列会在每次加入新元素时自动进行排序且时间效率高。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 priority_queue<LL,vector<LL>,greater<LL>> q; LL n,a,ans; int main () CI n; F (i,1 ,n) { CI a; q.push (a); } F (i,1 ,n-1 ) { LL a=q.top (); q.pop (); LL b=q.top (); q.pop (); ans+=a+b; q.push (a+b); } CO ans L; return 0 ; }
#Algo0106.# 于是他错误的点名开始了
题目描述
本题需要查找所给字符串是否存在,同时统计一个字符串被查找的次数。对于这种大批量查找字符串的操作,如果使用简单的对比,则会存在大量不必要的对比。所以需要使用字典树来快速查找字符串。由于题目需要统计一个字符串被查找的次数来判读是否存在重复点名,所以对字典树的节点进行改造,使其在记录是否为单词结尾的同时,记录该单词结尾是否被查找过。当该单词结尾被查找时,进行标记或返回被重复查找的信息。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 int n;string s; struct trie { int next[26 ]; int isEnd; int call; }tree[500005 ]; int inc;int insert (string s) int p=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s.size ();i++) { if (tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]) p=tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]; else { inc++; tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]=inc; p=inc; } } if (tree[p].isEnd) return 1 ; else tree[p].isEnd=1 ; return 0 ; } int check (string s) int p=0 ; for (int i=0 ;i<s.size ();i++) { if (!tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]) return 0 ; p=tree[p].next[s[i]-97 ]; } if (tree[p].call) return -1 ; if (!tree[p].isEnd) return 0 ; tree[p].call=1 ; return 1 ; } int main () CI n; F (i,1 ,n) { CI s; insert (s); } CI n; F (i,1 ,n) { CI s; switch (check (s)) { case 1 : CO "OK" L; break ; case 0 : CO "WRONG" L; break ; case -1 : CO "REPEAT" L; break ; } } return 0 ; }
#Algo0107.# Minimum Array
题目描述
对给定的b数组进行排序,使得数组c:\((a_i+b_i)%n\) 的字典序最小。使字典序最小,即尽量让0靠前,也就是\(b_i=n-a_i\) ,然后是数字小的靠前。所以可以使用可重复的集合multiset进行操作。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 int n,a[200005 ],ans,x;multiset<int > s; int main () CI n; CII (a,1 ,n) F (i,1 ,n) { CI x; s.insert (x); } F (i,1 ,n) { auto it=s.lower_bound (n-a[i]); if (it==s.end ()) it=s.begin (); CO (*it+a[i])%n P; s.erase (it); } CL return 0 ; }
#Algo0108.# 团伙
题目描述
本题的主要操作为合并集合以及判断两个元素是否在同一集合中,使用并查集即可。本题中“朋友的朋友是朋友”,将两个为朋友的元素所在集合进行合并即可。但是对于“敌人的敌人是敌人”,无法进行直接的合并。假设一个人的编号为a,总共n个人,则可以使用a+n来表示跟这个人是敌人关系。与这个人是敌人时,将第a+n个元素所在集合合并到自己的集合就可以表示敌人关系了,这时与a为敌人关系的人自然都处在了同一个集合。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 int n,m,x,y,ans;char c;int pre[200005 ];int find (int x) if (x!=pre[x]) pre[x]=find (pre[x]); return pre[x]; } void merge (int a,int b) int x=find (a); int y=find (b); pre[x]=y; } int main () CI n>>m; F (i,1 ,2 *n) pre[i]=i; F (i,1 ,m) { CI c>>x>>y; if (c=='E' ) { merge (x,y+n); merge (x+n,y); } else merge (x,y); } F (i,1 ,n) find (i); sort (pre+1 ,pre+n+1 ); F (i,1 ,n) if (pre[i]!=pre[i-1 ]) ans++; CO ans L; return 0 ; }
Part 3.Codeforces题解
题目链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1907
A. Rook
难度:800
根据输入,循环输出行和列并跳过棋子所在位置即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 int t,a;char c;int main () CI t; while (t--) { scanf ("\n%c%d" ,&c,&a); F (i,1 ,8 ) if (i!=a) CO c<<i L; F (i,97 ,104 ) if (i!=c) CO (char )i<<a L; } return 0 ; }
B. YetnotherrokenKeoard
难度:1000
遇到字符b时,删除其前面离他最近的一个小写字母,如果没有就不删除。遇到字母B时,删除其前面离他最近的一个大写字母,如果没有就不删除。
为了快速完成添加字符和删除字符的操作,可以维护两个栈,分别表示大写字母和小写字母,栈中存储着字符的位置。需要删除大小字母时,就弹出对应的栈顶元素,最后将两个栈存储到同一个数组然后从小到大排序,就可以得到最后的字符串。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 int t,ans[1000006 ];string s; stack<int > A,a; int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ),cin.tie (0 ),cout.tie (0 ); CI t; while (t--) { CI s; F (i,0 ,s.size ()-1 ) { if (s[i]=='b' ) { if (!a.empty ()) a.pop (); } elif (s[i]=='B' ) { if (!A.empty ()) A.pop (); } else { if (s[i]>='A' &&s[i]<='Z' ) A.push (i); else a.push (i); } } clear (ans); int t=0 ; while (!a.empty ()) { ans[t++]=a.top (); a.pop (); } while (!A.empty ()) { ans[t++]=A.top (); A.pop (); } sort (ans,ans+t); F (i,0 ,t-1 ) CO s[ans[i]]; CL } return 0 ; }
C. Removal of Unattractive Pairs
难度:1200
用桶来统计每个字母出现的次数,如果没有字母超过总数的一半,则总会被消除掉,如果超过了一半,则肯定有一部分该字母无法被消除掉
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 int t,n,a[26 ];string s; int main () CI t; while (t--) { clear (a); CI n; CI s; F (i,0 ,n-1 ) a[s[i]-97 ]++; int m=0 ; F (i,0 ,25 ) m=max (m,a[i]); CO max (n%2 ,2 *m-n) L ; } return 0 ; }
D. Jumping Through Segments
难度:1400
本题需要用二分查找,来找到一个最小的k。对于二分查找中的检查函数,可以求出人在当前k值下的移动范围与目标范围的交集,下一次以该交集为基础,求出人的最大移动范围与目标范围的交集并不断进行该步骤,如果其中任意一次求交集时发现并不存在交集,即人无法移动到目标位置,则当前k值无法得到答案。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 LL t,n,a[200005 ],b[200005 ]; int check (LL k) LL l=0 ,r=0 ; F (i,1 ,n) { l=max (l-k,a[i]); r=min (r+k,b[i]); if (l>r) return 0 ; } return 1 ; } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ),cin.tie (0 ),cout.tie (0 ); CI t; while (t--) { CI n; F (i,1 ,n) CI a[i]>>b[i]; LL l=0 ,r=1e9 ; while (l<=r) { LL mid=(l+r)/2 ; if (check (mid)) r=mid-1 ; else l=mid+1 ; } CO l L; } return 0 ; }